Fits (seizures)
Fits, seizures and convulsions generally mean the same thing.
Seeing a child or young person having a fit can be frightening. Most fits do not cause serious harm. The commonest type of fit in children is a febrile convulsion. This is a fit associated with a high temperature. This sort of fit tends to occur in younger children. Fits sometimes occur without a fever (afebrile fit or seizure). If your child has had only one afebrile fit, it does not always mean they have epilepsy. Many children will never have another one.
First aid for a convulsive seizure:
A convulsive seizure is where the child is stiff or shaking. The information below can help you to focus when your child is having a seizure. It can help you to give first aid to keep them safe:
Do
• Stay calm
• Protect them from injury (remove harmful objects from nearby)
• Cushion or gently hold your child’s head to protect them from head injury
• Note the date and time the seizure started. If stiffness and jerking continues for 5 minutes or more you should call 999 for an ambulance
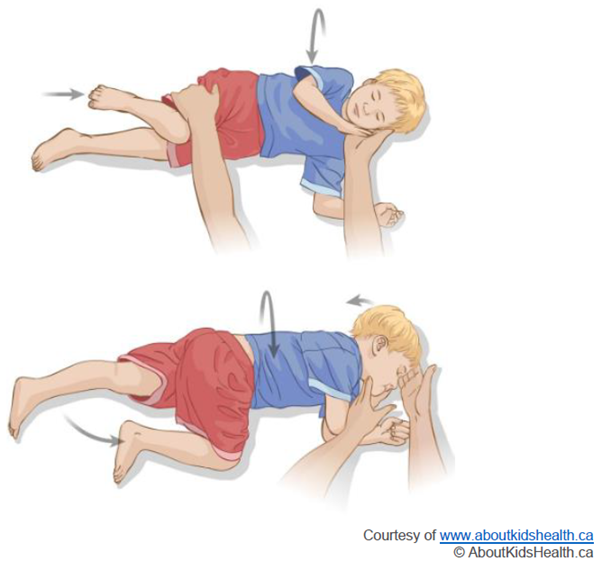
• Turn your child onto their side, into the recovery position (see below) as soon as you are able (as shown in Image 1). This can help with their breathing and help if they vomit or have other types of fluid in their mouth. Some noisy breathing and slight colour change is common
• If possible, try to video the seizure on a mobile phone as it can provide a lot of useful information to your child’s doctor or nurse. Video can help confirm the type of seizure which then helps decide which tests and treatment may be needed. Try to capture the whole child in the video, say out loud what you are seeing and show how they respond to you
• Stay with your child until they are fully recovered
• Your child may be confused, drowsy or fall asleep after a seizure. Reassure them if they are confused, let them rest or sleep if they are drowsy, make sure you keep an eye on them until they are fully recovered
Do not
• Restrain or restrict your child’s movements
• Move your child unless they are in danger
• Put anything in their mouth
• Give your child anything to eat or drink until they have fully recovered
Call 999 for an ambulance if:
• The stiffness or jerking continues for 5 minutes or more
• One seizure follows another before your child has fully recovered
• Your child is injured, or you are worried about their breathing
Moving a child into the recovery position:
When should you worry?
If your child has any of the following:
-
Is under 1 year of age
-
The first time your child has had a fit (seizure)
-
Has a fit that lasts longer than 5 minutes
-
They have one fit after another without being awake in between
-
They are seriously injured during the fit
-
Remains drowsy or confused more than an hour after their fit
-
Has weakness of the arms or legs, visual difficulties (double vision) or difficulty speaking after the fit has stopped
-
They have trouble breathing after the fit has stopped
-
Breathing very fast or breathing that stops or pauses
-
Working hard to breathe, drawing in of the muscles below the rib, unable to talk or noisy breathing (grunting)
-
Becomes pale, blue, mottled and/or unusually cold to touch
- Develops a rash that does not disappear with pressure and seems unwell (see the ‘Glass Test’)
You need urgent help
Go to the nearest Hospital Emergency (A&E) Department or phone 999
If your child has any of the following:
-
Has another fit (less than 5 minutes) within the same illness
-
Breathing a bit faster than normal or working a bit harder to breathe
-
Noisy breathing (stridor) only when upset
-
Dry skin, lips, tongue or looking pale
-
Not had a wee or wet nappy in last 8 hours
-
Poor feeding in babies (less than half of their usual amount)
-
Irritable (unable to settle them with toys, TV, food or hugs even after their fever has come down)
-
A temperature 39°C or above in babies 3-6 months
-
Temperature of 38°C or above for more than 5 days or shivering with fever (rigors)
-
Getting worse or you are worried about them
You need to contact a doctor or nurse today
Please call your GP surgery or contact NHS 111 - Go to 111.nhs.uk or call 111.(111 online does not currently take questions about children aged under 5, so if your child is 4 or younger, please call 111).
If symptoms persist for 4 hours or more and you have not been able to speak to either a member of staff from your GP practice or to NHS 111 staff, recheck that your child has not developed any red features.
If none of the above features are present:
Seizure lasting less than 5 minutes with full recovery in a child with previous febrile convulsions or known epilepsy.
-
Watch them closely for any change and look out for any red or amber symptoms
-
If your child has a long term condition or disability and you are worried please contact your regular team or follow any plans that they have given you
Self care
Continue providing your child’s care at home. If you are still concerned about your child, call NHS 111 – dial 111
What should you do?
When the fit stops, you can give them paracetamol or ibuprofen. However, this might not stop them having another one. Always follow instructions on the container and do not exceed daily maximum doses.
For more information on fever please see our page here
Fits associated with fever (febrile convulsion)
Febrile convulsions occurs in some children with a high temperature (fever). Although it can be extremely scary the first time you see your child have one, most of the time they are not serious. Most occur with common illnesses such as ear infections, colds and other viral infections. Full recovery with no permanent damage is usual. The main treatment is aimed at the illness that caused the fever.
Who gets them?
-
They occur in about 1 in 20 children, most commonly between 6 months and 6 years of age
-
They often occur on the first day of an illness associated with fever. There appears to be no connection between how high a child’s fever is and whether they have a fit. They can occur even with mild fevers
-
Most children will not have another fit during the same illness
-
1 in 3 children who have a febrile convulsion may go on to have further febrile convulsions in the future. This is more likely if other members of the family have had febrile convulsions.
-
Febrile convulsions are not epilepsy. Regular treatment for prevention of future fits is usually not necessary. There is a small risk of your child developing epilepsy in the future and many parents worry about this, however, most children who have childhood simple febrile convulsions grow out of them and do not develop epilepsy
-
If your child has had a previous febrile convulsion, has a clear cause for their fever, their seizure stops quickly and they are back to normal soon after, they may be cared for at home. The first time your child has a fit, you should go to your local Emergency Department or call an ambulance
-
Once they have been examined, if a cause is found and your child is well, it may be appropriate that they are discharged to continue recovering at home
Fits not associated with fever (afebrile fits and seizures):
If your child has had only one afebrile fit, it does not always mean they have epilepsy. Some children will never have another one.
Children can have events that look very similar to a seizure, but they are not; these include faints, tics, day dreams, sleep disorders and breath-holding attacks. However, if your child has more than one fit, they will need to investigate for possible epilepsy.
How long will the symptoms last?
In most cases, children with simple febrile convulsions appear dazed and their eyes may roll back.
Their bodies may go stiff, their arms and legs may twitch or shake and they will become unresponsive for a few seconds. It is unusual for the febrile convulsion to last for more than 5 minutes.
Your child may be sleepy for a few minutes afterwards.
Where should you seek help?
- If it is non-urgent, speak to your local pharmacist or health visitor
- If your child has any of the above features, urgently see your GP. For an urgent out-of-hours GP appointment, call NHS 111
- You should only call 999 or go to your nearest Emergency Department (A&E) in critical or life threatening situations
For wear and tear, minor trips and everything in between
Self-care
You can treat your child's very minor illnesses and injuries at home.
Some illnesses can be treated in your own home with support and advice from the services listed when required, using the recommended medicines and getting plenty of rest.
Sound advice
Children can recover from illness quickly but also can become more poorly quickly; it is important to seek further advice if a child's condition gets worse.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
Pharmacists are experts in many aspects of healthcare and can offer advice on a wide range of long-term conditions and common illnesses such as coughs, colds and stomach upsets. You don’t need an appointment and many have private consultation areas, so they are a good first port of call. Your pharmacist will say if you need further medical attention.
Sound advice
- Visit a pharmacy if your child is ill, but does not need to see a GP
- Remember that if your child's condition gets worse, you should seek further medical advice immediately
- Help your child to understand - watch this video with them about going to the pharmacy
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
The 0-19 Service for children and young people is delivered by Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust and offers a single point of access for Health Visiting, School Nursing and the Family Nurse Partnership. You can contact the teams using the details below:
Single Point of Access (SPA): 01865 903 800
Email: cyp0-19@oxfordhealth.nhs.uk
Chat Health Parentline
Text us any time for confidential advice and support and you will have a response the next working day (Monday-Friday exluding Bank Holidays).
Parents and carers for children aged 0-4: Text 07312 263 081
Parents and carers of children aged 5-11: Text 07312 263 227
Young people aged 11-19 and their parents and carers: Text 07312 263 08
Health Visitors
Health visitors are registered nurses or midwives who have additional training in community public health nursing. They provide a universal service, targeted to individual needs for children aged 0-5 years. Learn more about the Oxfordshire Health Visiting Service here!
School and college Health Nurses
School Health Nurses are specialist public health nurses and have offices across Oxfordshire. They work very closely with Health Visitors to support school aged children. They are available for young people to access in secondary schools and colleges, and offer a service to children who are home educated. They work closely with children, young people and their families to support and promote health and wellbeing. Learn more about the Oxfordshire School and college Health Nursing Service here!
Family Nurse Partnership
The Family Nurse Partnership service supports parents who are aged 19 years or under at conception, or under 21 years if they have been in care. The Family Nurse works alongside younger parents in their home, offering health, wellbeing and development support and information from the early stages of pregnancy, usually up until your child is two. Learn more about the Family Nurse Partnership service here!
GPs assess, treat and manage a whole range of health problems. They also provide health education, give vaccinations and carry out simple surgical procedures. Your GP will arrange a referral to a hospital specialist should you need it.
Sound advice
You have a choice of service:
- Doctors or GPs can treat many illnesses that do not warrant a visit to A&E
- Help your child to understand – watch this video with them about visiting the GP or going to a walk in centre
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
If you’re not sure which NHS service you need, you can call 111 or use 111 online.
Please note that 111 online is for people aged 5 and over. Call 111 if you need help for a child under 5.
An adviser will ask you questions to assess your symptoms and then give you the advice you need, or direct you straightaway to the best service for you in your area.
Sound advice
Use NHS 111 if you are unsure what to do next, have any questions about a condition or treatment or require information about local health services
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
Emergency Departments (A&E) provide vital care for life-threatening emergencies, such as loss of consciousness, suspected heart attacks, breathing difficulties, or severe bleeding that cannot be stopped. If you’re not sure it’s an emergency, call 111 for advice.





